- Expert consensus on fibrin sealant aneurysm sac filling during endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysmal repair
- Auxiliary liver transplantation using discarded liver: innovative clinical applications and future perspectives
- Applied anatomy of segmental Glissonian pedicles at the hepatic hilum guided by the Laennec's membrane concept and its value in laparoscopic surgery
- Application of augmented reality navigation combined with indocyanine green fluorescence imaging in laparoscopic resection of central hepatic tumors
- Expression characteristics of FGL1 in peritumoral tissues of hepatocellular carcinoma and its association with prognosis
- Impact of prophylactic inferior mesenteric artery embolization on outcomes after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: a single-center retrospective analysis
- Vascular trauma management from the perspectives of international guidelines and Chinese consensus: an integrated interpretation of the 2025 ESVS guidelines and the Chinese expert consensus
- Comparison of venous access strategies for endovascular management of central venous stenosis or occlusion in hemodialysis patients
- Novel technology for lower esophageal sphincter augmentation: indications and limits in current surgical practice
- Chinese expert consensus on thyroid reoperation
- Feasibility and safety analysis of mixed reality-assisted surgery for substernal goiter: a report of 29 cases
- Prevention and management of bleeding in endoscopic thyroid surgery
- Clinical evaluation of the single-tunnel transmural puncture method in small-incision transoral endoscopic thyroidectomy vestibular approach
- Exploration and reflection on robotic complex rectal cancer surgery
- Current Issue
- Published Ahead-of-Print
- Virtual Issues
- Previous Issues
-
Alliance of Chinese Expert Consensus on Postoperative Adjuvant Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Chinese College of Surgeons, Committee of Liver Cancer, Chinese Anti-Cancer Association, Liver Cancer Group, Society of Oncology, Chinese Medical Association
2026,35(1):1-20, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.260017
Abstract:
Recurrence and metastasis after surgery remain major determinants of long-term survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and to date, no universally accepted postoperative adjuvant therapy has been established to effectively prevent recurrence. In recent years, postoperative adjuvant strategies involving systemic antitumor therapies—represented by targeted agents and immune checkpoint inhibitors—used alone or in combination with locoregional therapies have been actively explored. The Alliance of Chinese Expert Consensus on Postoperative Adjuvant Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, together with the Chinese College of Surgeons, the Committee of Liver Cancer of the Chinese Anti-Cancer Association, and the Liver Cancer Group of the Society of Oncology of the Chinese Medical Association, convened experts from relevant disciplines to review and synthesize updated evidence. Through multiple rounds of discussion and revision, the Expert consensus on postoperative adjuvant therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma (2026 edition) was formulated. This consensus aims to systematically summarize the available evidence on postoperative adjuvant therapy for HCC, integrate current clinical practice, and provide practical guidance for clinicians, with the goal of improving postoperative survival outcomes in patients with HCC.
-
LI Yongjun, ZHAO Jichun, ZHAO Yu, ZHANG Lan, HUANG Jianhua, GUO Pingfan, WANG Tao, ZHANG Long, WANG Haiyang, CHEN Quan,
2026,35(1):21-31, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.260002
Abstract:
Lower extremity arteriosclerosis obliterans, also known as peripheral artery disease (PAD), is a chronic arterial occlusive disease characterized by atherosclerosis affecting the arteries of the lower extremities, leading to luminal stenosis or occlusion, and consequently resulting in ischemia and necrosis of the lower limbs. PAD not only significantly reduces patients' quality of life but also carries a non-negligible risk of amputation and mortality, imposing a heavy economic and health burden on both patients and society, especially among the elderly. Advanced age has been identified in multiple studies as a key risk factor for amputation and death in PAD patients. The prevalence of PAD in the elderly increases significantly with age, as they often have multiple coexisting conditions such as coronary artery disease, renal insufficiency, and tumors. Consequently, the pathophysiological characteristics, treatment options, and prognostic assessments are more complex compared to those of younger patients. Diagnostically, because comorbidities can often mask the symptoms of PAD in elderly patients, a comprehensive approach involving detailed medical history, physical examination, and auxiliary tests is required. In terms of treatment, the management of elderly patients with PAD is further complicated by issues such as poor adherence to therapy and difficulties in follow-up, which increase the challenges in clinical management. Currently, there is a lack of specific national or international guidelines or consensuses focused on the diagnosis and treatment of PAD in the elderly. To address this gap, the "Chinese expert consensus on the management of lower extremity atherosclerotic disease in the elderly" has been developed. This consensus integrates the latest evidence-based medical data and clinical experience, with a focus on key issues in elderly PAD patients, such as disease characteristics, comorbidity management, personalized treatment, and long-term follow-up. It aims to establish scientific and practical diagnostic and therapeutic standards to provide guidance for clinicians.
-
Vascular Surgery Professional Committee of the Chinese Association of Rehabilitation Medicine
2026,35(1):32-43, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250679
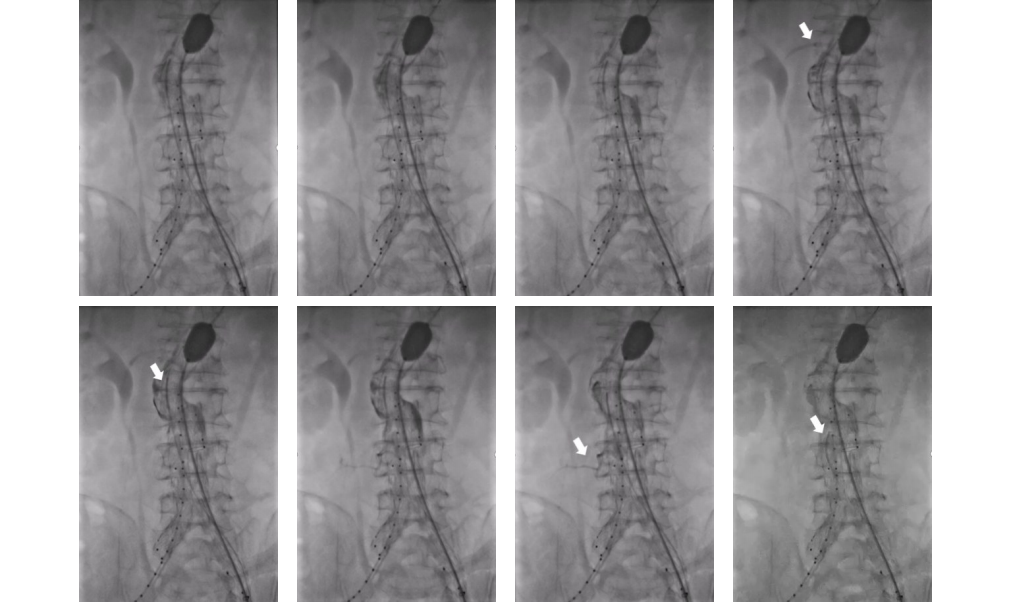
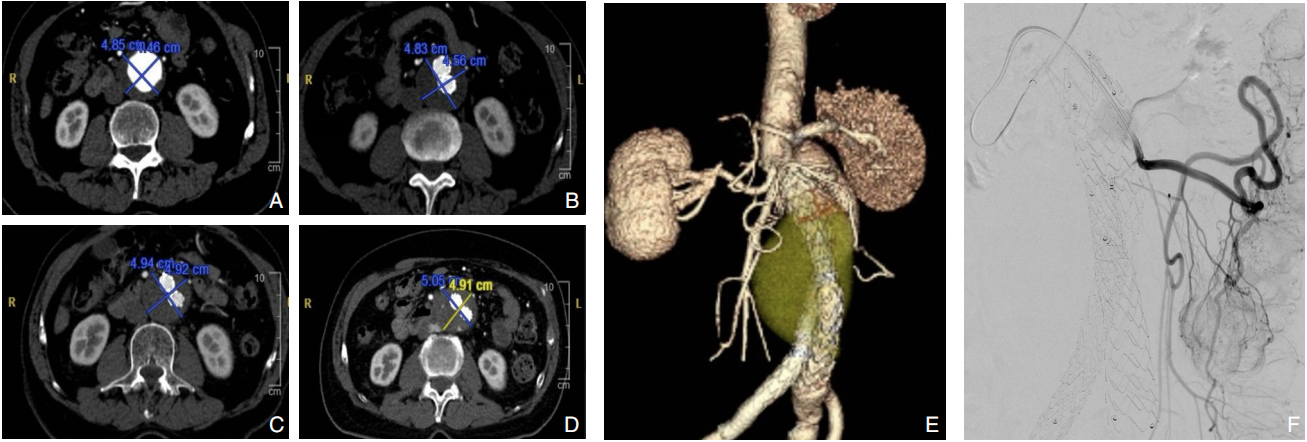
Abstract:
Abdominal aortic aneurysm is a potentially fatal vascular disease commonly encountered in the elderly population. Although endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) has become the preferred treatment modality, the incidence of postoperative endoleaks remains high (20%-40%), with more than 30% of cases requiring secondary interventions, thereby significantly compromising long-term outcomes. To standardize the application of fibrin sealant aneurysm sac filling during EVAR, the Vascular Surgery Professional Committee of the Chinese Association of Rehabilitation Medicine convened a multidisciplinary expert panel. In accordance with the RIGHT reporting guideline and the GRADE evidence grading system, and through two rounds of Delphi surveys to prioritize clinical questions combined with systematic evidence review, the committee developed the Expert consensus on fibrin sealant aneurysm sac filling during endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysmal repair. This consensus systematically addresses key aspects including indications and contraindications, technical procedures, dosage estimation, intraoperative assessment criteria, prevention and management of complications, and postoperative follow-up. It defines criteria for complete sac filling and provides tailored application strategies under various anatomical conditions. The aim of this consensus is to standardize clinical practice, reduce the incidence of endoleaks, improve long-term outcomes after EVAR, and provide vascular surgeons with evidence-informed and practically applicable guidance.
-
2026,35(1):44-52, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250589
Abstract:
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the malignancies with high incidence and mortality rates in China. Approximately 64% of patients are diagnosed at intermediate or advanced stages at initial presentation (CNLC stages IIb, IIIa, and IIIb), and most have already lost the opportunity for curative treatment. Conversion therapy aims to enable initially unresectable HCC patients to become eligible for surgical resection or liver transplantation through effective interventions, thereby improving long-term outcomes. Yttrium-90 microsphere selective internal radiation therapy (90Y-SIRT) has demonstrated unique advantages in HCC conversion therapy, owing to its potent local tumor control, induction of future liver remnant hypertrophy, promotion of portal vein tumor thrombus regression, and favorable safety profile with preservation of quality of life. This article systematically reviews the application of 90Y-SIRT in conversion therapy prior to liver resection and liver transplantation, summarizes its mechanisms of action, clinical evidence, and combination treatment strategies, and discusses current challenges and future directions, with the aim of providing references for clinical decision-making and research in HCC conversion therapy.
-
YUAN Shengxian, DING Dongyang, ZHOU Weiping
2026,35(1):53-59, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250551
Abstract:
Primary liver cancer, specifically referring to hepatocellular carcinoma (hereafter referred to as HCC) in this article, is one of the malignant tumors with relatively high incidence and mortality in China. Because most patients are diagnosed at an intermediate or advanced stage, or present with impaired hepatic reserve due to underlying liver cirrhosis, opportunities for curative surgical resection are limited. In recent years, drawing on therapeutic experience from colorectal cancer, conversion therapy has attracted considerable attention in the field of liver cancer as a comprehensive treatment strategy aimed at achieving radical resection. Through systemic therapy, locoregional treatment, or their combination, this approach seeks to convert initially unresectable HCC into tumors amenable to radical resection, thereby improving long-term survival outcomes. With the rapid development of targeted therapies, immunotherapy, and locoregional treatment modalities, conversion therapy has become a major research focus in liver cancer management in China and has achieved encouraging progress in clinical practice. Nevertheless, substantial controversies remain regarding patient selection, the value of surgery after conversion, optimal timing of resection, and postoperative management. In this article, recent advances in oncological conversion therapy are systematically reviewed and critically appraised, with the aim of promoting conceptual consensus and standardized clinical implementation of conversion therapy, ultimately improving the overall treatment outcomes of patients with intermediate to advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.
-
SHI Hanying, ZHOU Yang, LIN Kongying, ZENG Yongyi
2026,35(1):60-68, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250693
Abstract:
Medical digital biopsy (MC-Biopsy) is a data integration and application framework developed in the context of the growing convergence of artificial intelligence and large-scale clinical data, aiming to address the fragmentation and limited reusability of heterogeneous clinical information in real-world practice. Centered on standardized data governance, MC-Biopsy systematically integrates laboratory results, imaging, pathology, clinical narratives, and longitudinal follow-up data to construct a disease-specific, multimodal database covering the entire disease course, while embedding artificial intelligence-based methods into existing clinical data structures and workflows to facilitate the transformation of high-value clinical data into reusable evidence. Taking the MC-Biopsy framework preliminarily established and implemented at our institution as an example, this article describes its overall concept, core technical architecture, and real-world deployment, with a particular focus on its application in key scenarios of liver disease management, including risk stratification of high-risk populations, tumor diagnosis and staging, treatment response assessment, and prognosis evaluation. In practice, MC-Biopsy supports individualized and stratified risk management by integrating established models such as the aMAP (age-Male-ALBi-Platelets score) into outpatient and follow-up workflows and by linking longitudinal laboratory and imaging data. In addition, natural language processing-based structuring of clinical narratives contributes to improving data quality and supporting standardized clinical training. Through multimodal integration of imaging, pathology, and clinical data, a traceable digital phenotype repository is progressively established, enabling liver disease research to shift from single-modality, static indicator-based analyses toward multidimensional investigations grounded in longitudinal disease trajectories and real-world outcomes. From the perspective of discipline development, this study further discusses the potential role of MC-Biopsy in problem-oriented translational research and interdisciplinary medical education. Overall, MC-Biopsy represents a reproducible and scalable technical reference with the potential to support precision clinical care, real-world research, and the development of learning healthcare systems.
-
ZUO Bangyou, YANG Chong, YOU Xinyu, HE Qian, CHENG Donghui, QIU Guoteng, LI Dexin, WU Gang, ZHANG Yu
2026,35(1):69-76, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.260012
Abstract:
Discarded liver refers to functional liver segments separated from resected diseased livers. When used as small-volume grafts in auxiliary liver transplantation, discarded livers provide a novel strategy for expanding the donor pool. In recent years, with the further extension of the discarded liver concept, the rational integration of discarded liver transplantation with staged hepatectomy and other surgical techniques, together with rapid advances in the field of xenotransplantation, has offered additional therapeutic options for patients awaiting liver transplantation. How to achieve innovative clinical applications of discarded livers, as well as the prospects and directions for their wider adoption, has become an important issue in the field of liver transplantation. Based on current domestic and international evidence and the authors'clinical experience, this paper systematically summarizes the technical evolution and current applications of auxiliary liver transplantation using discarded livers, with a particular focus on innovative surgical strategies, the potential clinical value of combining discarded liver transplantation with xenotransplantation, and future perspectives on the safe implementation and individualized surgical decision-making of this approach.
-
CHANG Guijian, ZHUO Xinbin, LEI Wendi, XIE Minhua, HUANG Jian, ZHANG Yong, HUANG Jianmin, LIN Dexin
2026,35(1):77-87, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250378
Abstract:
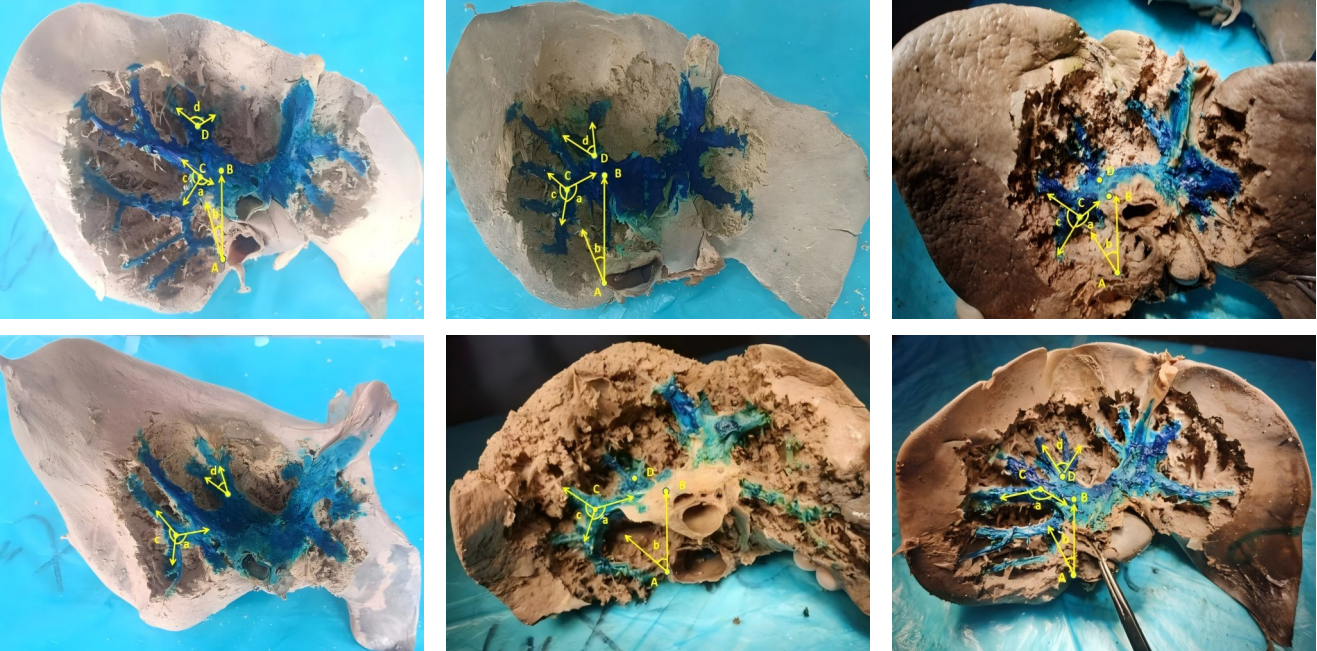
Background and Aims Precise identification and control of segmental Glissonian pedicles are fundamental to laparoscopic anatomical liver segmentectomy. However, marked anatomical variations, particularly in the right hemiliver, pose significant technical challenges. Based on the anatomical concept of the hepatic Laennec's membrane, this study aimed to systematically investigate the applied anatomy of Glissonian pedicles at the hepatic hilum and to establish practical anatomical landmarks for laparoscopic anatomical liver resection.Methods Six intact adult human liver specimens without macroscopic lesions were dissected under the guidance of the Laennec's membrane concept. The segmental Glissonian pedicles at the first porta hepatis were meticulously isolated, and the intervening liver parenchyma was removed. The origin, branching patterns, and spatial courses of Glissonian pedicles in each hepatic segment were analyzed. For the right hemiliver, a localization system consisting of four anatomical landmarks, two reference lines, and four characteristic angles was proposed and quantitatively evaluated using specimen measurements combined with CT imaging and three-dimensional liver reconstruction.Results The intrahepatic Glissonian system demonstrated both consistent patterns and pronounced individual variations. In the left hemiliver, the Glissonian pedicles of segments Ⅱ and Ⅲ usually arose independently, while segment Ⅳ commonly presented a bifurcated pattern with occasional multiple branches. In contrast, the right hemiliver showed substantial variability: segment V pedicles were frequently multibranched and often received contributions from segment Ⅵ; segment Ⅵ served as a pivotal pedicle with multiple branches contributing to segments V and Ⅶ; segment Ⅶ most commonly originated from the root of the right posterior pedicle, although in some cases it was formed by distal extensions of segment Ⅵ; segment Ⅷ pedicles were relatively constant in morphology, typically consisting of one or two branches. The proposed anatomical landmarks and quantitative parameters enabled clearer spatial localization of segmental Glissonian pedicles in the right liver.Conclusion Systematic dissection of segmental Glissonian pedicles guided by the Laennec's membrane concept, together with a quantitative anatomical landmark system, enhances the understanding of their spatial anatomy and variations. This approach provides practical and reliable anatomical guidance for precise and safe laparoscopic anatomical liver segmentectomy.
-
SHEN Zhengchao, CHEN Zhiyuan, XI Shihang, PAN Xuan, QIAN Daohai, MUHAMMAD Danish Irshad, WANG Xiaoming
2026,35(1):88-96, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250468
Abstract:
Background and Aims Laparoscopic resection of centrally located hepatic tumors remains technically demanding due to the complex anatomical relationships with major vascular structures. Conventional intraoperative ultrasound or indocyanine green fluorescence imaging (ICG-FI) alone has limitations, particularly in visualizing deep anatomical structures. This study aimed to evaluate the clinical value of augmented reality (AR) navigation combined with ICG-FI in laparoscopic resection of central hepatic tumors.Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on 38 consecutive patients who underwent laparoscopic resection of central hepatic tumors guided by AR navigation combined with ICG-FI between May 2022 and March 2025. Intraoperative navigation performance, surgical parameters, and perioperative outcomes were assessed.Results All 38 procedures were completed laparoscopically without conversion. The intraoperative tumor fluorescence detection rate was 100%. The mean operative time was (324.9 ± 132.4) min, and the median intraoperative blood loss was 400 (50-1 200) mL. The mean registration error was (6.3±0.6) mm. The median number of predicted and verified vessels was 6 (4-8) and 7 (5-10), respectively. R0 resection was achieved in all patients, with a mean surgical margin of (1.5±0.5) cm. The postoperative complication rate was 13.2%, with no severe complications such as intra-abdominal hemorrhage, gas embolism, or liver failure. The median postoperative hospital stay was 9 (4-20) days. During a median follow-up of 20 months, no tumor recurrence was observed.Conclusion The combined use of AR navigation and ICG-FI enables intraoperative prediction and verification of critical vascular structures and facilitates precise control of the transection plane in laparoscopic resection of central hepatic tumors. This technique improves surgical precision and safety and shows promising clinical potential.
-
ZHOU Xinrun, CHEN Zhongjian, FENG Li, LI Ben
2026,35(1):97-104, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250546
Abstract:
Background and Aims Surgical resection remains the preferred curative treatment for patients with solitary hepatocellular carcinoma (≤5 cm) complicated by liver cirrhosis. However, optimal strategies regarding surgical approach and resection margin width remain controversial due to limited hepatic functional reserve in these patients. This study aimed to evaluate the impact of surgical methods and margin width on postoperative prognosis, identify independent prognostic factors, and develop a prognostic prediction model to support clinical decision-making.Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on 280 patients with solitary hepatocellular carcinoma ≤5 cm in diameter complicated by liver cirrhosis who underwent surgical treatment between January 2020 and June 2022. After excluding patients lost to follow-up, 272 cases were included in the final analysis. Patients were stratified into favorable and poor prognosis groups based on 3-year postoperative outcomes. Differences in clinical characteristics, tumor features, and surgery-related variables between the two groups were compared. Multivariate Logistic regression analysis was performed to identify independent prognostic factors, on the basis of which a prognostic prediction model was established and its predictive performance was evaluated using ROC curve analysis.Results Multivariate Logistic regression analysis demonstrated that non-anatomical hepatectomy (OR=4.221, 95% CI=2.031-8.732), resection margin width of 0.5-1 cm (OR=2.863, 95% CI=1.542-5.318) or <0.5 cm (OR=5.155, 95% CI=2.481-10.692), Child-Pugh grade B (OR=3.127, 95% CI=1.451-6.723) and grade C (OR=6.890, 95% CI=2.132-22.351), increased tumor diameter (OR=1.891, 95% CI=1.211-2.952), and macrovascular invasion (OR=3.781, 95% CI=1.653-8.672) were identified as independent risk factors for poor postoperative prognosis (P<0.05). The Logistic prediction model achieved an area under the ROC curve of 0.935 (95% CI=0.892-0.978), with a sensitivity of 90.21%, a specificity of 86.45%, and an optimal cut-off value of 0.46.Conclusion For patients with solitary hepatocellular carcinoma ≤5 cm accompanied by liver cirrhosis, anatomical hepatectomy with a resection margin of at least 1 cm is associated with improved postoperative outcomes when hepatic functional reserve permits. The proposed prognostic model provides a valuable tool for individualized surgical planning and risk stratification.
-
YE Taozhu, YU Rui, LIN Dakui, PENG Jianchao, HUANG Xinghua, HU Huanzhang
2026,35(1):105-113, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250592
Abstract:
Background and Aims In cirrhotic patients undergoing radical hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the technique used for hepatic transection may influence perioperative outcomes and long-term prognosis. This study compared argon plasma coagulation (APC) with a conventional electrosurgical knife (EK) in terms of postoperative complications and survival outcomes.Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on 204 cirrhotic HCC patients who underwent radical hepatectomy in the 900th Hospital of PLA Joint Logistic Support Force between January 2013 and January 2020. Patients were divided into an APC group (n=103) and an EK group (n=101) according to the method used for hepatic transection. Perioperative outcomes, postoperative complications, overall survival (OS), and recurrence-free survival (RFS) were compared between groups.Results Baseline characteristics were comparable between the two groups (all P>0.05). The incidence of post-hepatectomy liver failure was significantly lower in the APC group than that in the EK group (0.0% vs. 5.9%, P=0.036), as was the intraoperative transfusion rate (12.6% vs. 23.8%, P=0.039). No significant differences were observed in postoperative day 1 liver function parameters, overall complications, or severe complications (all P>0.05). Survival analysis demonstrated significantly higher 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS and RFS rates in the APC group compared with the EK group (OS: P=0.034; RFS: P=0.003). Recurrence pattern analysis showed that no margin recurrence was observed in the APC group, whereas eight cases occurred in the EK group (P=0.011).Conclusion In cirrhotic patients undergoing radical hepatectomy for HCC, APC is associated with reduced PHLF and intraoperative transfusion without increasing perioperative morbidity, and is correlated with improved OS and RFS. These findings suggest that APC may provide oncological and safety advantages, warranting further validation in prospective multicenter studies.
-
HU Chunyan, SUN Haoting, LIU Xiaojia, JIA jie, WANG Chaoqun
2026,35(1):114-123, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.260010
Abstract:
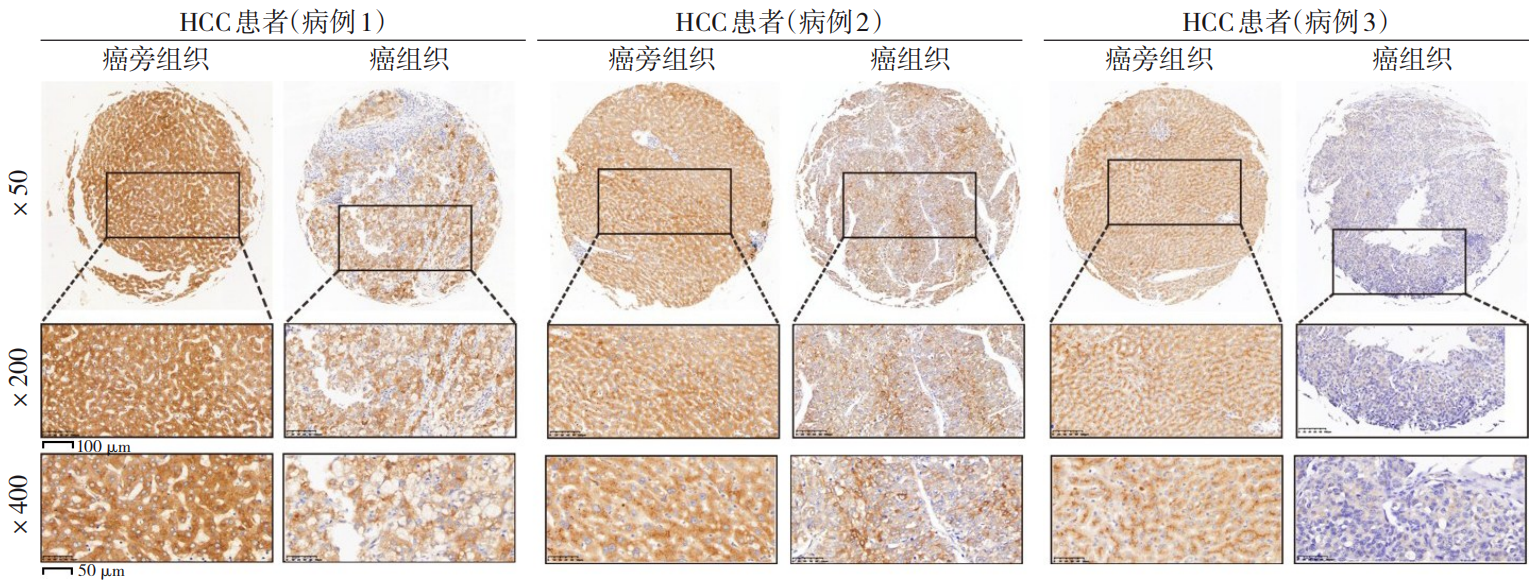
Background and Aims Liver cancer exhibits marked biological heterogeneity, and reliable prognostic biomarkers remain limited. Fibrinogen-like protein 1 (FGL1), a liver-specific secreted protein and a major ligand of lymphocyte activation gene 3 (LAG-3), has emerged as a critical regulator of tumor immunity. This study aimed to evaluate the expression pattern of FGL1 in peritumoral tissues and its prognostic significance in liver cancer patients after curative resection.Methods A total of 183 patients with liver cancer who underwent curative resection at Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, between January 2010 and December 2013 were retrospectively collected. FGL1 expression levels in peri-tumoral and tumor tissues were detected by immunohistochemistry and quantified using the H-score method. Expression patterns were further validated using data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. The optimal cutoff value for FGL1 expression was determined using maximally selected rank statistics. Survival differences between patients with high and low peritumoral FGL1 expression were compared, and independent prognostic factors were evaluated using Cox proportional hazards regression models.Results Both TCGA data and clinical samples demonstrated significantly higher FGL1 expression in peritumoral tissues compared with tumor tissues (both P<0.05). Patients were stratified into high- and low-expression groups based on the optimal cutoff value. High peritumoral FGL1 expression was significantly associated with poorer disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) rates (both P<0.05). Multivariate Cox analysis identified peritumoral FGL1 overexpression as an independent predictor of DFS (HR=1.689, 95% CI=1.010-2.823, P=0.046) and OS (HR=1.733, 95% CI=1.112-2.702, P=0.015).Conclusion FGL1 expression is significantly elevated in peritumoral tissues of HCC and independently predicts unfavorable postoperative outcomes. Peri-tumoral FGL1 may serve as a novel prognostic biomarker and a potential therapeutic target in the FGL1/LAG-3 immune axis.
-
YAN Jiayan, WANG Jiayi, FENG Hao, YANG Kaini, ZHU Zexin, ZHANG Junzhe, BU Junfeng, HU Jiaming, GAO Si, TANG Shuibin, HUANG Ao, CHEN Tao, HUA Rong, SUN Yongwei, LIU Yingbin, FAN Jia, ZHOU Jian, CHEN Wei
2026,35(1):124-140, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250635
Abstract:
Background and Aims The hepatic vascular and biliary systems exhibit substantial anatomical variability and complex spatial relationships, posing challenges for precise surgical planning based on conventional two-dimensional imaging. This study aimed to evaluate the clinical value of three-dimensional visualization in characterizing the spatial architecture of hepatic vasculature and bile ducts and to explore its association with hepatic volumetric distribution.Methods A total of 610 living liver donors and 158 patients with bile duct dilatation were retrospectively analyzed. Three-dimensional models of the hepatic artery, portal vein, hepatic veins, and bile ducts were reconstructed from contrast-enhanced CT images. Vascular and biliary anatomical patterns, spatial relationships, and their correlations with hepatic lobe and segmental volumes were systematically assessed.Results Three-dimensional visualization enabled intuitive and comprehensive depiction of hepatic vascular and biliary anatomy. Distinct portal vein configurations were associated with significant differences in regional liver volume distribution, with an increased proportion of the right posterior lobe observed in patients with specific portal vein branching patterns. The presence of an inferior right hepatic vein with a diameter ≥5 mm was also associated with a larger right posterior lobe volume. Analyses of extrahepatic and intrahepatic spatial relationships revealed relatively consistent positional patterns between the right hepatic artery, portal vein, and bile ducts, and a significant correlation was observed between the spatial courses of the right hepatic artery and the right posterior bile duct.Conclusion Three-dimensional visualization provides accurate preoperative assessment of hepatic vascular and biliary anatomy and clarifies complex spatial relationships and their volumetric implications. This technique offers critical anatomical support for precision hepatobiliary surgery and liver transplantation.
-
ZHANG Liyuan, YAN Sijie, YANG Yitian, XIE Jiayuan, TANG Yangshuo, ZHANG Bo
2026,35(1):141-148, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250622
Abstract:
Background and Aims Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) presenting initially with bone metastasis is uncommon, and metastasis to the appendicular skeleton is particularly rare. These cases often lack typical liver disease history, elevated alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), or characteristic imaging findings, leading to frequent misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis. This study reports a rare case of occult HCC presenting with humeral metastasis and reviews the literature to improve clinical recognition and management.Methods The clinical data of a 42-year-old male patient presenting with humeral metastasis as the initial manifestation admitted in August 2025 were retrospectively analyzed, including laboratory tests, multimodal imaging findings, histopathological and immunohistochemical results, treatment, and follow-up outcomes. Relevant literature was also reviewed.Results The patient presented with left shoulder pain. Imaging revealed osteolytic destruction of the left humerus. PET/CT incidentally detected multiple hepatic lesions without significant FDG uptake. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound demonstrated atypical enhancement patterns, initially suggesting a perivascular epithelioid cell tumor. Histopathological and immunohistochemical examination of biopsy specimens from both the humeral and hepatic lesions confirmed moderately differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma with humeral metastasis (CNLC stage IIIb). The patient received systemic therapy with sintilimab plus bevacizumab, followed by transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. After 6 months of follow-up, the intrahepatic lesions had decreased in size, the bone metastasis remained stable, and pain symptoms were significantly relieved.Conclusion HCC presenting with humeral metastasis as the initial manifestation is extremely rare and may lack typical imaging and serological features. Clinicians should consider HCC in patients with unexplained bone metastasis even in the absence of liver disease history or elevated AFP. Multimodal imaging and pathological biopsy are essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
-
LAO Jianqiang, LI Wenyang, HUANG Chaoman, WU Jiaxin, YANG Xiaozhuang, OU Qi, MO Fujie, PAN Yanxi, PENG Ningfu, ZHONG Jianhong, LIAO Yingyang
2026,35(1):149-161, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250649
Abstract:
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most prevalent malignancies worldwide, with a poor prognosis and high mortality. In recent years, the approval of novel targeted agents and immunotherapies, together with the advancement of multidisciplinary management, has led to continuous updates of HCC clinical practice guidelines. Owing to differences in epidemiology, etiological factors, and clinical practice patterns, substantial variations exist among guidelines regarding HCC screening, diagnosis, staging, and treatment. This review systematically compares and interprets the recommendations of major guidelines released between 2023 and 2025, including those from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the British Society of Gastroenterology, the European Association for the Study of the Liver, the European Society for Medical Oncology, and the Chinese Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Primary Liver Cancer. By highlighting their similarities and differences, this article aims to provide practical insights for optimizing HCC management in China.
-
FU Shibo, LAI Jianlin, HUANG Long, TIAN Yifeng, CHEN Shi
2026,35(1):162-168, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250414
Abstract:
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, demonstrates marked heterogeneity in biological behavior and therapeutic response. Emerging evidence indicates that tumor capsule integrity, a classical histopathological feature, plays a pivotal role in risk stratification and treatment decision-making. Preoperative assessment primarily relies on imaging modalities, whereas histopathology remains the gold standard. According to structural integrity, the capsule can be categorized as complete, incomplete, or absent. An intact capsule functions as a physical barrier that limits tumor invasion and is closely associated with a lower incidence of microvascular invasion. In surgical management, narrow-margin resection may be considered in capsule-intact tumors when negative margins are secured, whereas wider margins are recommended for tumors with incomplete or absent capsules. Beyond surgery, capsule integrity has been correlated with therapeutic response to transarterial chemoembolization, radiotherapy, and systemic therapies, potentially through mechanisms involving tumor hemodynamics, microenvironmental modulation, and oncogenic signaling pathways as a bridge linking tumor biology with therapeutic strategies. Tumor capsule status warrants further investigation in the era of precision medicine.
-
WEN Luyu, GAN Xuemei, CAO Yang, ZHANG Xin, LI Ruiqi, ZHANG Yulu, LIU Hong
2026,35(1):169-179, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250317
Abstract:
Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent form of programmed cell death driven by lipid peroxidation and plays a critical role in the initiation, progression, and therapeutic resistance of liver cancer. In recent years, both basic and translational studies focusing on the regulatory network of ferroptosis have advanced substantially. This article systematically reviews the molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis in liver cancer, its subtype heterogeneity, and its interactions with the tumor microenvironment. Particular emphasis is placed on the central roles of the system Xc--GSH-GPX4 axis, dysregulated iron metabolism, and lipid remodeling pathways in ferroptosis regulation in liver cancer. From a therapeutic perspective, ferroptosis inducers, either as monotherapy or in combination with chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and radiotherapy, have demonstrated synergistic antitumor potential, with some strategies entering early-phase clinical evaluation. In addition, ferroptosis-related biomarkers, such as ACSL4 and FDFT1, are increasingly recognized for their value in prognostic stratification and treatment response prediction. Further studies are warranted to elucidate the dynamic interplay between ferroptosis and the tumor microenvironment, refine biomarker systems, and optimize clinical trial design, thereby accelerating the translational application of ferroptosis-targeted strategies in precision therapy for liver cancer.
-
2026,35(1):180-186, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250293
Abstract:
背景与目的 DICER1综合征是一种由DICER1基因胚系突变引起的罕见常染色体显性遗传性肿瘤易感综合征,可累及多器官并表现为多种良恶性肿瘤或增生性病变。肾外肾母细胞瘤、多结节性甲状腺肿及Sertoli-Leydig(S-L)细胞瘤均为其相关表型,但三者同时出现的病例尚未见报道。本文报告1例同时合并上述三种表型的DICER1综合征患者,并结合文献进行分析,以提高对该综合征复杂临床谱系的认识。方法 回顾性分析1例女性患者的临床资料,包括临床表现、影像学检查、手术经过、病理学及免疫组化结果、基因检测及家庭谱系图分析结果;同时检索并总结近30年相关文献,对具有肾母细胞瘤、结节性甲状腺肿及S-L细胞瘤等表型的DICER1综合征病例进行归纳分析。结果 患者9岁时因腹痛行右侧卵巢肿瘤切除术,病理诊断为原发性卵巢畸胎样肾外肾母细胞瘤,术后行辅助化疗。3年后因甲状腺结节行右侧甲状腺切除术,病理为多结节性甲状腺肿。半年后因左侧盆腔新发肿块行卵巢囊肿剥除术,病理提示低分化S-L细胞瘤。基因检测发现DICER1基因外显子8 c.904-1G>C杂合突变,其父亲为同位点杂合突变携带者。结合临床表现及分子遗传学结果,确诊为DICER1综合征。随访3年未见复发或新发病灶。文献复习显示,同时合并上述三种表型的病例尚未见报道。结论 DICER1综合征临床表型多样且诊断具有挑战性。当患儿出现多器官肿瘤或罕见肿瘤组合时,应警惕遗传性肿瘤综合征的可能,尽早开展基因检测及家系筛查。早期识别DICER1综合征对于制定个体化治疗策略及开展长期监测随访具有重要意义。
-
2026,35(1):187-191, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250638
Abstract:
背景与目的 原发性结肠黏膜黑色素瘤极为罕见,恶性程度高,易发生淋巴及远处转移,预后不佳,临床诊断困难。本文报告1例结肠回盲部原发性黏膜黑色素瘤病例,并结合文献复习,总结其临床特征、诊断要点、治疗策略及预后情况,以提高对该罕见疾病的认识。方法 回顾性分析1例经手术及病理证实的结肠回盲部原发性黏膜黑色素瘤患者的临床资料,包括临床表现、影像学及内镜特征、病理与免疫组化结果、分子检测结果、治疗经过及随访情况,并结合相关文献进行综合分析。结果 患者为52岁女性,2023年11月7日因“间断性右下腹痛3个月”入院。腹部增强CT提示回盲部占位并周围淋巴结肿大;肠镜见巨大结节状肿物充满肠腔,活检提示恶性黑色素瘤。行右半结肠切除术(D2)。术后病理示肿瘤侵犯黏膜层及深肌层,伴脉管内瘤栓,淋巴结转移5/20。免疫组化示S-100、SOX10、Melan-A及HMB45阳性,Ki-67约50%。基因检测提示BRAFV600E突变。术后患者拒绝辅助治疗。术后16个月发现肠系膜区淋巴结转移,23个月出现颈部淋巴结转移,目前随访24个月,仍存活并持续随访。文献复习显示,该病多见于中老年女性,临床表现缺乏特异性,确诊依赖病理及免疫组化,手术切除为无远处转移患者的主要治疗方式。结论 结肠回盲部原发性黏膜黑色素瘤罕见且侵袭性强,早期诊断困难,易发生淋巴转移。确诊需排除转移性黑色素瘤并结合免疫组化及分子检测结果。对于无远处转移患者,根治性手术切除是首选治疗方式,分子靶向治疗及免疫治疗可能成为改善预后的重要方向。
-
2026,35(1):192-197, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250531
Abstract:
背景与目的 在政策推动与医疗效率提升需求的背景下,日间手术模式在我国迅速发展。患者就医体验作为衡量医疗质量与服务成效的重要指标,其影响因素尚缺乏系统分析。本研究旨在探讨日间手术患者就医体验的现状及其主要影响因素,为优化服务流程与提升管理质量提供依据。方法 采用回顾性横断面研究设计,提取中南大学湘雅医院日间手术中心2024年3月—2025年3月电子化满意度调查数据。经纳排标准筛选后,共纳入4 531例有效样本。采用描述性统计分析患者总体满意度水平,运用独立样本t检验及单因素方差分析比较不同人口学特征患者的评分差异,采用皮尔森相关分析及多元线性回归分析探讨各服务维度对总体就医体验的独立影响。结果 4 531例患者中,总体就医体验评分为10者占86.63%,评分≥9者占95.41%,整体满意度较高。不同性别、年龄、文化程度及就诊专科患者的就医体验评分差异均无统计学意义(均P>0.05)。相关分析显示,医护人员技术水平、信息告知、健康教育、疑问解答、病室环境及就医流程等因素均与总体就医体验呈明显正相关(均P<0.01)。多元线性回归分析结果表明,就医流程(β=0.362)、日间病房医生技术水平(β=0.164)、病室环境(β=0.118)、门诊预约岗护士服务态度及护理技术等因素为独立影响因素(均P<0.05);而日间病房护士服务态度、手术医生服务态度及日间病房医生病情告知对总体体验无明显影响(均P>0.05)。结论 日间手术患者总体就医体验良好。优化就医流程、强化医护人员专业技术能力与有效沟通、改善病室环境,是提升患者体验与推动日间手术高质量发展的关键路径。